Alpha International Education
- Events
- BPA
- RBC × Alpha
- HOSA
- TED-Ed Student Talks
- The Duke of Edinburgh Award
- THRIVE Investment Challenge
- Brain Bee
- 2025 Summer Camp
- …
- Events
- BPA
- RBC × Alpha
- HOSA
- TED-Ed Student Talks
- The Duke of Edinburgh Award
- THRIVE Investment Challenge
- Brain Bee
- 2025 Summer Camp
Alpha International Education
- Events
- BPA
- RBC × Alpha
- HOSA
- TED-Ed Student Talks
- The Duke of Edinburgh Award
- THRIVE Investment Challenge
- Brain Bee
- 2025 Summer Camp
- …
- Events
- BPA
- RBC × Alpha
- HOSA
- TED-Ed Student Talks
- The Duke of Edinburgh Award
- THRIVE Investment Challenge
- Brain Bee
- 2025 Summer Camp
Alpha International Education
Should you study abroad in Canada?
Why study abroad in Canada?
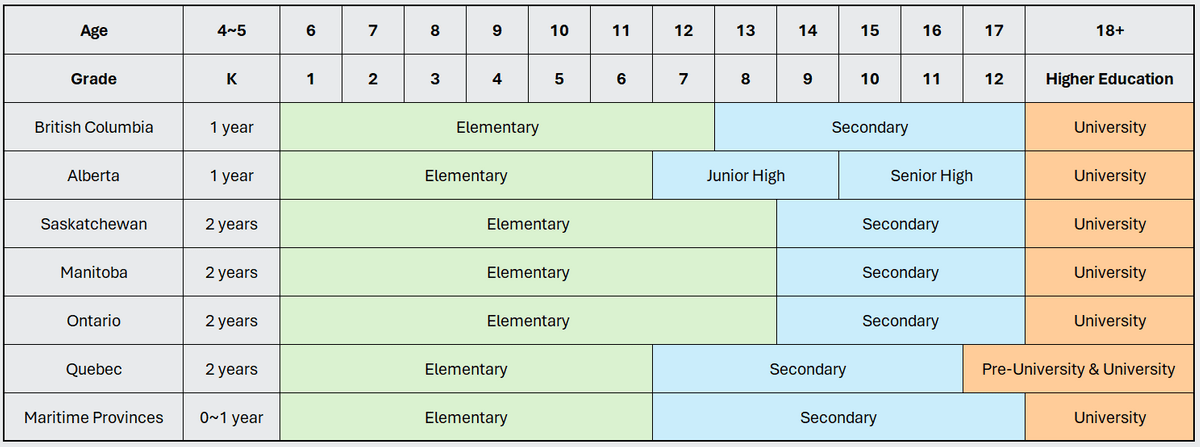
Higher education in Canada is public and therefore regulated by the state and government, which results in high educational quality, rigorous standards, excellent academic outcomes, and a particular reputation for technological innovation. In addition to the many world-renowned universities, Canadian has colleges that are more oriented towards preparing and training students for employment by offering career skills-oriented programs. Both types of institutions are widely recognized in Canadian society.
British Columbia
British Columbia (BC) is home to several world-renowned universities, such as the University of British Columbia (UBC), Simon Fraser University (SFU), and the University of Victoria (UVic). Approximately one-third of Chinese students studying abroad in Canada are in BC.
BC's education system and high school graduation requirements:
BC has a seven-year elementary school and five-year secondary school system. Students must earn at least 80 credits in a three-year program in grades 10-12, four credits per course, including: 48 credits of required courses, 28 credits of elective courses, and 4 credits of a program of educational and career goals; at least 16 of these credits should be earned in the grade 12 program.
For BC students, Canadian universities require provincial exam results for enrolment in addition to the usual high school grades (mainly grade 12).
International students are also required to complete a two-year program before they are allowed to enter university.
Ontario
Ontario (ON) houses the largest Canadian city, Toronto, as well as the capital of Canada, Ottawa. It is also where many world-class universities are located, including the University of Toronto, Queen's University, McMaster University, University of Waterloo, University of Western Ontario, York University, University of Ottawa, and Wilfrid Laurier University.
Ontario's education system and high school graduation requirements:
Ontario adopts a four-year high school system for grades 9-12. To attend university, students need to receive the Ontario High School Diploma, which requires the completion of 30 credits in high school (18 required course credits and 12 elective course credits; one credit is given per course), as well as at least 40 hours of volunteering.
In addition, students must pass the Ontario Secondary School Literacy Test (OSSLT) in order to attend university.
Alberta
Alberta (AB) is Canada's strongest economic province and has an educational base that is among the highest in Canada and even the world. The University of Alberta is located in Edmonton, the provincial capital.
Alberta's education system and high school graduation requirements:
Alberta has a 6-3-3 education system, with high school being grades 10-12. A high school diploma requires students to complete a minimum of 100 credits, with 5 credits for each course passed. The 100 credits must include the following required courses: Grade 12 English (30 level), Grade 12 Social Science (30 level), Grade 11 Mathematics (20 level), Grade 11 Science or Chemistry or Biology or Physics (20 level), Grade 10 Physical Education, as well as Career and Life Management (CALM).
Quebec
Quebec (QC) has a relatively special status in Canada, as its official language is French and it hosts the largest concentration of French-speaking population in North America. One of the best universities in Canada, McGill University, is located in Montreal, the largest city in Quebec.
Quebec's education system and high school graduation requirements:
The education system in Quebec is slightly different from the previous three provinces. There are 6 years of elementary school, 5 years of secondary school (3 years of junior high school and 2 years of senior high school), 2 years of pre-university or 3 years of vocational specialization, and finally university education.
Quebec's 5 year secondary education leads to either a Diploma of Secondary Studies (DES) or a Diploma of Vocational Studies (DEP). High school students must complete a minimum of 54 credits in the fourth and fifth years of high school to receive the DES, and 20 of these 54 credits must be from fifth year courses.
High school graduates are first enrolled in the General and Professional Teaching College (CEGEP), where they can choose between a two-year pre-university program that prepares them for university education, or a three-year technology education program, which allows them to work as technicians and craftspeople.